Salvage procedures
1. Treatment
A salvage procedure is a complete removal of the affected bone and teeth with reconstruction and closure of the soft tissues. This allows for a comfortable and functional bite. This is a maxillectomy or incisivectomy procedure (depending on the location).
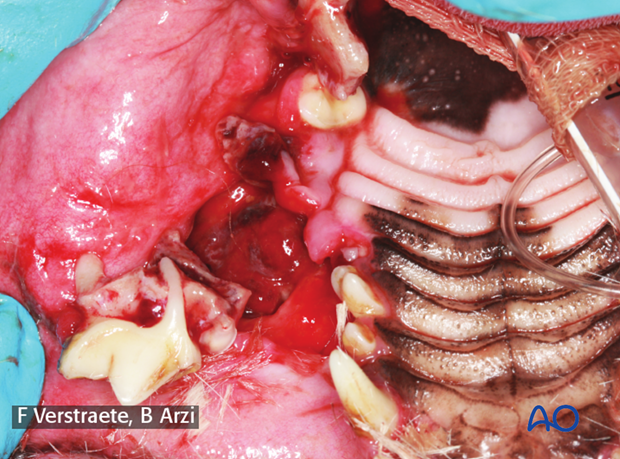
2. Positioning and approach
This procedure is performed through the intraoral approach to the hard palate, with the patient placed in dorsal recumbency.
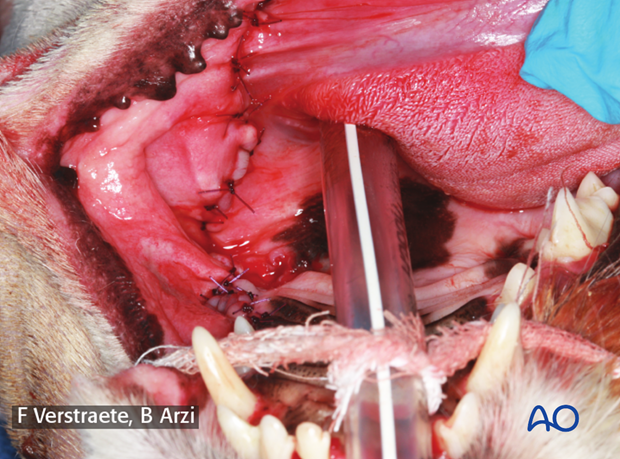
3. Closure
Prior to closure, the area should be inspected for teeth, bone, and dental calculus that may have dislodged into the nasal cavity. Copious irrigation with sterile saline is advised to reduce the possibility of infection and flap dehiscence.
Closure of the flap can be done in one or two layers using a 4-0/5-0 poliglecaprone 25, or other monofilament absorbable suture, in a simple-interrupted fashion.
4. Aftercare
The dog should be kept on soft food for one or two weeks after surgery.
Intraoperative intravenous administration and then oral antibiotics for one to two weeks is recommended. Antibiotics used should have an excellent oral cavity penetration and spectrum. Example: ampicillin at 20 mg/kg intravenous antibiotics followed by oral antibiotics amoxicillin/clavulanic acid at 15-20 mg/kg orally twice daily.
Pain medication, such as opioids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, are used for 7-14 days.
If the fracture involved the oral cavity, oral rinse with 0.05-0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate solution is recommended (not for maxillomandibular fixation).
Recheck is recommended in 10-14 days and at three and six months post-surgery.
If there are any signs of complications (i.e. purulent nasal discharge), CT and rhinoscopy are indicated.












