Patient examination: Neurological evaluation
1. Classification
Neurological injuries at sacral level are classified as follows:
- Nx: Cannot be examined
- N0: No neurological deficits
- N1: Transient neurological injury
- N2: Nerve root injury
- N3: Incomplete Cauda Equina Syndrome
2. Lumbo-sacral nerve root injury
Before undertaking definitive treatment of sacral fractures, it is essential to know the functional status of the patient's lumbosacral nerve roots. A careful and detailed examination is necessary, to assess perineal sensation.
Neurologic abnormalities should be correlated with anatomic site of injury:
- If a lumbo-sacral nerve deficit is present in extra sacral injuries, further investigation and possible treatment must be considered.
- If a sacral nerve deficit is present with a sacral fracture, the nerves may need decompression with fracture reduction and/or sacral laminectomy.
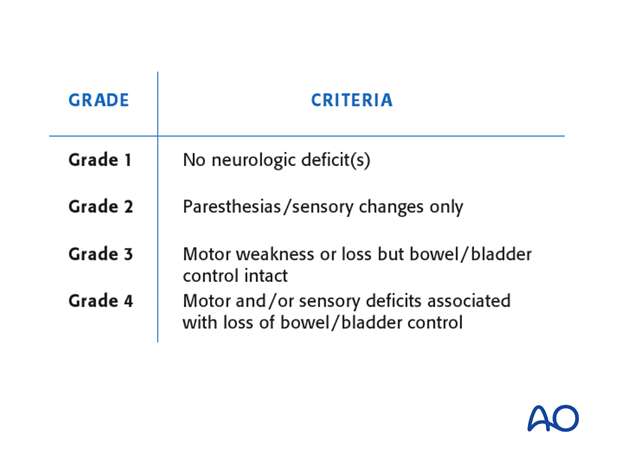
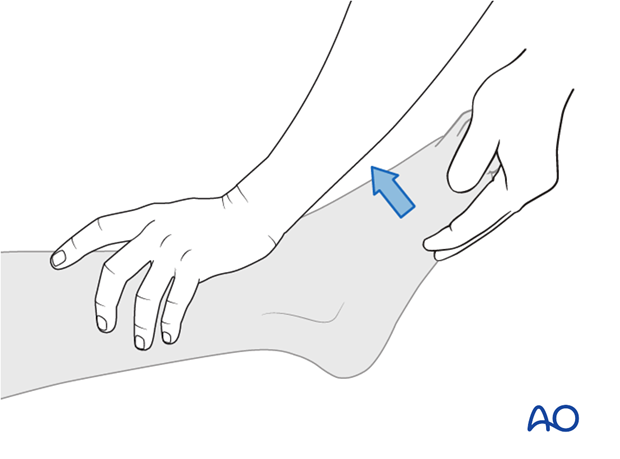
3. Motor function
There are six levels of muscle strength, ranging from 0 – 5, as indicated on the INSCI assessment sheet.

Ankle dorsiflexors (L4)
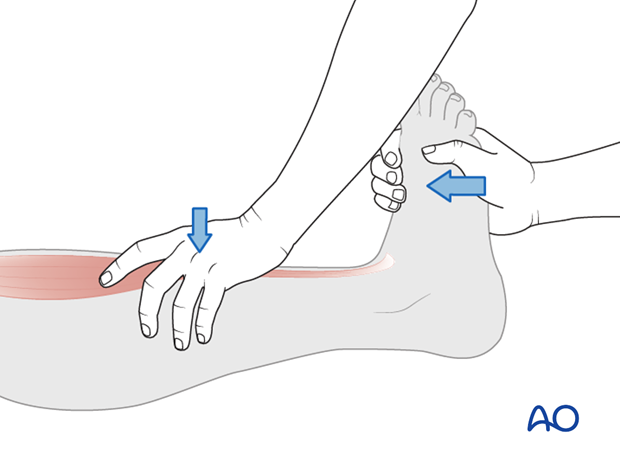
Great toe extensors (L5)
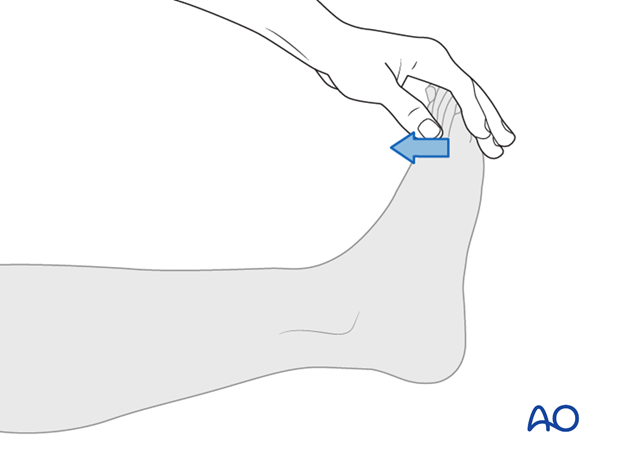
Ankle plantar flexors (S1)
4. Sensory function
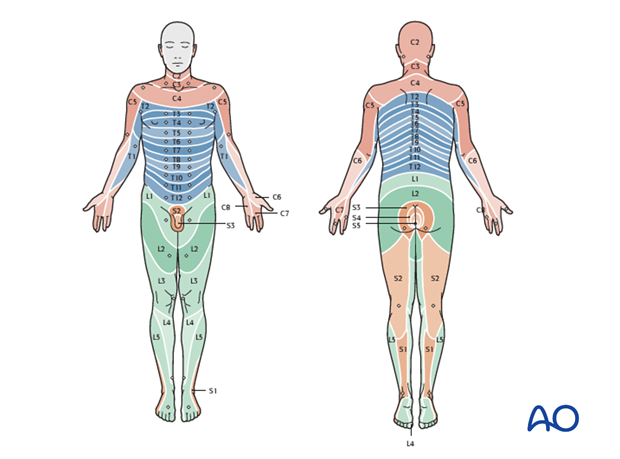
Pin prick sensation is assessed with a needle. Light touch sensation is assessed with a piece of tissue paper.
Sensation is scored as absent (0), abnormal (1), or normal (2).
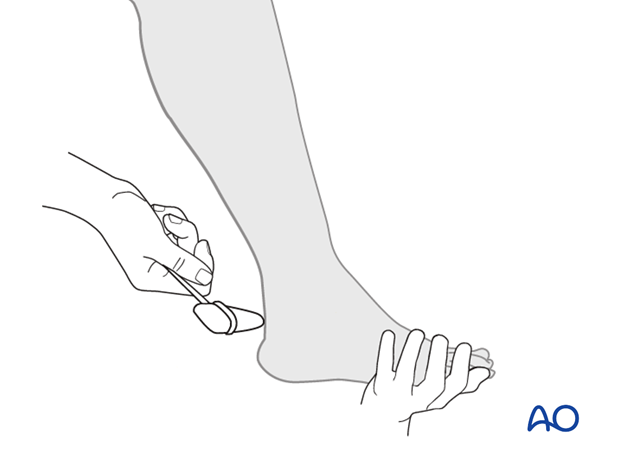
5. Reflex examination
Achilles tendon (S1).
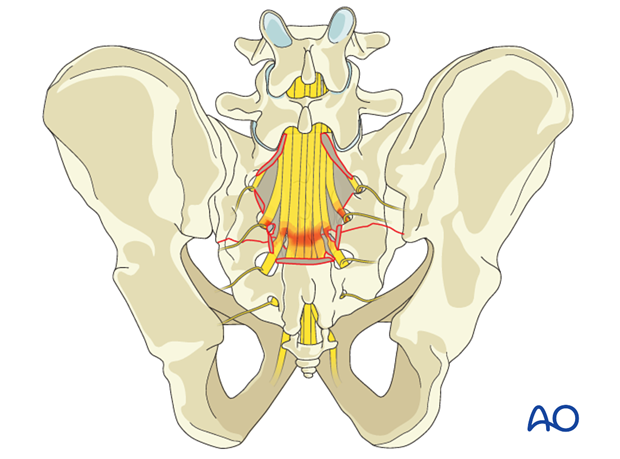
The S2-5 dermatomes should be assessed for pin prick and light touch sensation (diagram, dermatome).
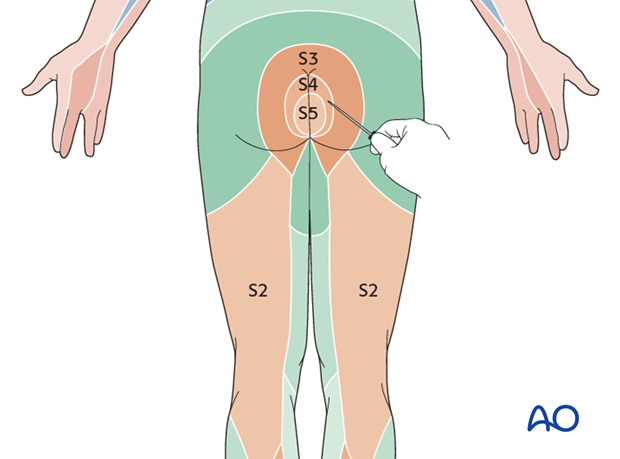
In the Cauda Equina Syndrome there is an injury to the spinal rootlets
Clinical presentation:
- Bowel and bladder dysfunction
- motor deficits