Medial approach to the proximal forearm: Hotchkiss over the top
1. Introduction
The Hotchkiss “over the top” approach is the most anterior of the medial approaches and provides good access to the tip of the coronoid process and the whole anterior elbow joint.
2. Medial approaches
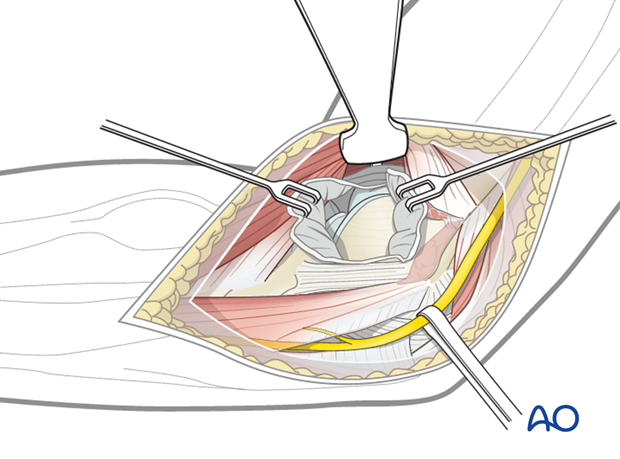
The interval that splits the flexor-pronator mass and elevates the anterior part (pronator teres (PT), flexor carpi radialis (FCR), and palmaris longus (PL)) along with brachialis from the anterior elbow capsule gives good access to the anterior elbow capsule and the tip of the olecranon also known as the Hotchkiss “over the top” approach (1). The access to the medial facet of the coronoid is limited and there is also poor access to the base of the coronoid.
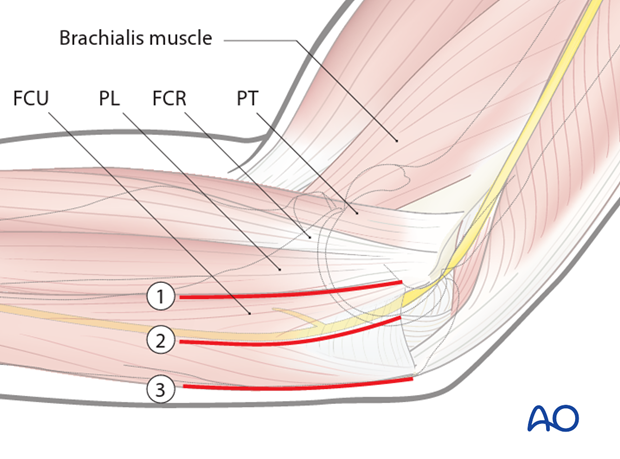
For access to the medial facet, use the interval where the ulnar nerve lies between the heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU split; 2).
For access to the base consider elevating the entire flexor-pronator mass from posterior to anterior (Taylor and Scham; 3).
In the following the Hotchkiss over the top approach is described.
Skin incision
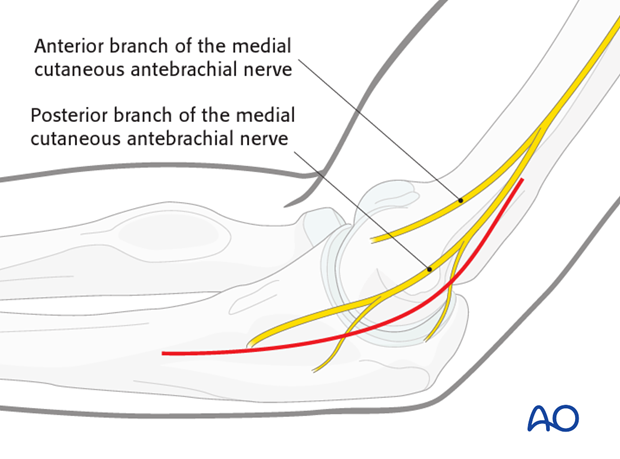
The skin incision can either be posterior with a medial skin flap or direct medial, taking care to protect branches of the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve which travels more anteriorly.
Ulnar nerve
The ulnar nerve should be identified and protected. Generally, it is unroofed for 6 centimeters proximal and distal. Consider anterior subcutaneous transposition if you think this will keep the nerve safer.
Pearl: Always start with the exposure of the ulnar nerve proximally. It is easier and safer to identify the ulnar nerve proximally.
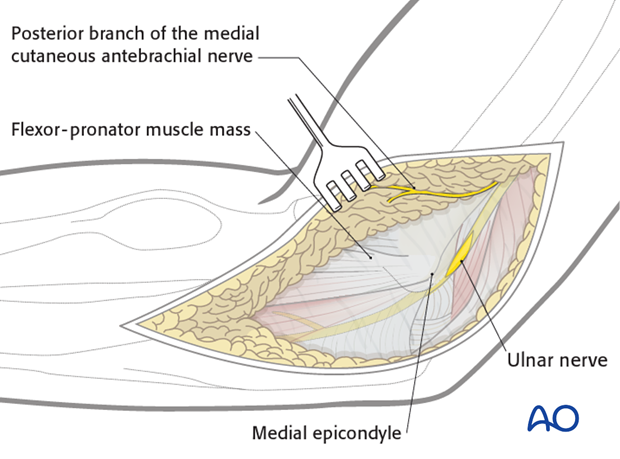
Follow the ulnar nerve distally as it goes under the fascia between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU). Incise it with a pair of scissors and protective the first motor branch running to the humeral part of the FCU.
Pearl: Small, bleeding vessels can be best coagulated by using a bipolar coagulation pincette to protect the ulnar nerve.
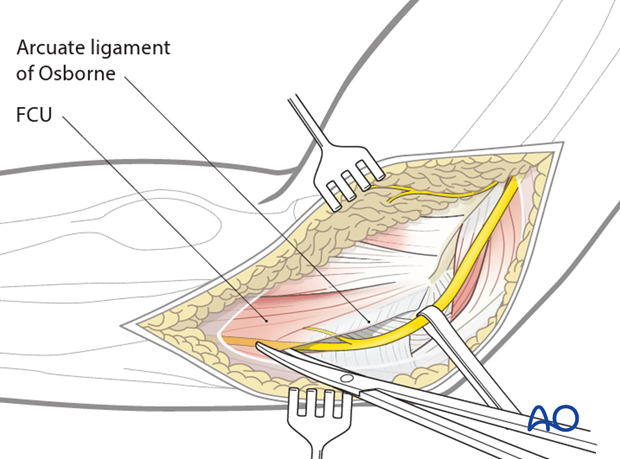
Splitting the flexor-pronator mass
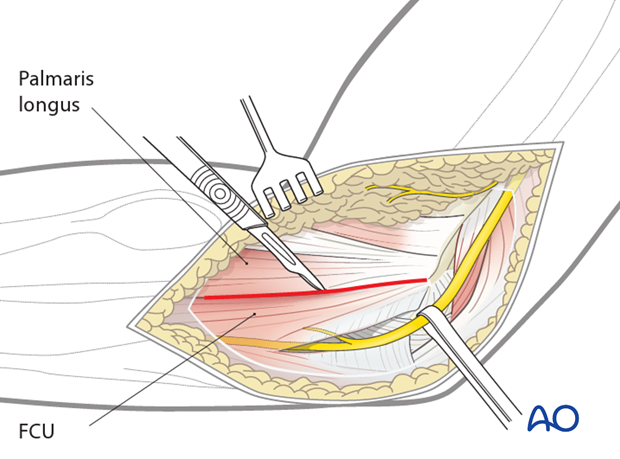
Use blunt dissection to identify the anterior edge of the flexor-pronator mass, over the top of the brachialis and near to where the median nerve and brachial artery lie. With the ulnar nerve identified posteriorly, the flexor-pronator mass can be split, usually in the middle of the anterior-posterior width, but sometimes more posteriorly to get better access to the anteromedial coronoid. Elevate the palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis and pronator teres origins off the medial epicondyle.
Extend this dissection proximally by extra-periosteal dissection of the brachialis muscle and the flexor-pronator mass off the medial supracondylar ridge of the distal humerus and the anterior elbow capsule.
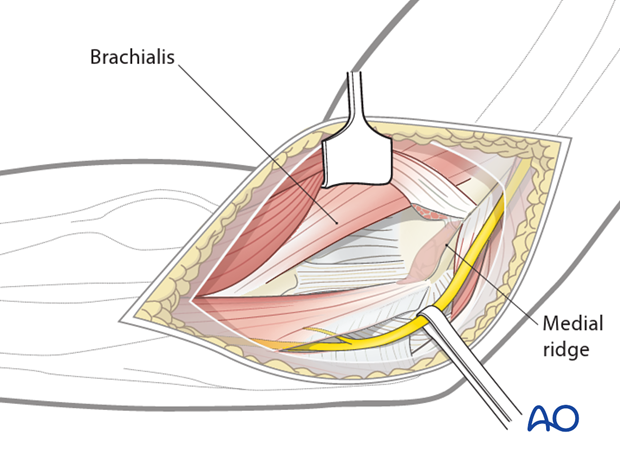
Using blunt Hohmann retractors, the exposure can be improved across the entire anterior elbow joint.
One can split the pronator mass more distally for better exposure to the medial coronoid, for instance if a longer plate fixation is planned.
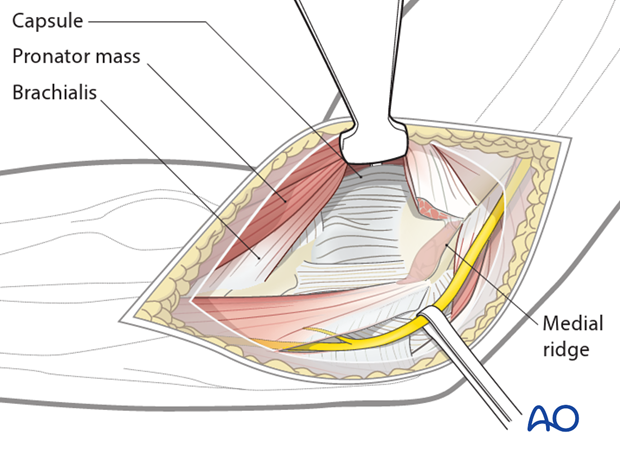
Capsulotomy
The elbow joint can be entered with an anterior capsulotomy or capsulectomy depending on the circumstances.