Nonoperative treatment
1. Treatment principles
Nonoperative treatment is reserved for medically infirm patients that cannot tolerate any surgical intervention.
Initial treatment is symptomatic with bed rest and pain management.
Patients with intracapsular fractures generally tolerate mobilization before patients with extracapsular fractures.
Therefore, skin traction may be appropriate for intracapsular fractures, but most patients with trochanteric fractures will benefit from at least 2 weeks of skeletal traction before any attempt to mobilize from bed to chair.
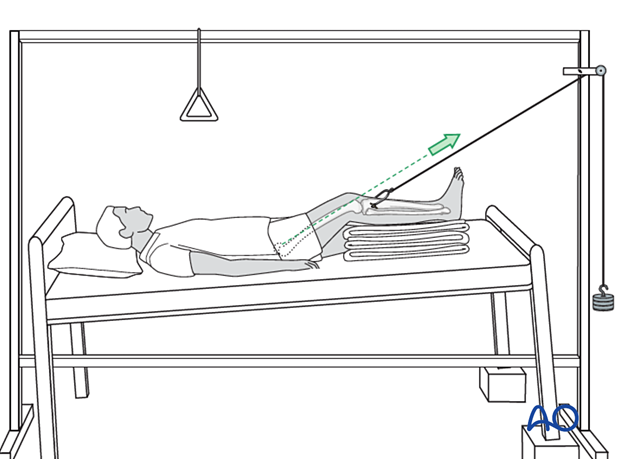
2. Skeletal traction
The application of skeletal traction for a few weeks may be used for pain relief.
Use about 5 kg of weight for traction.
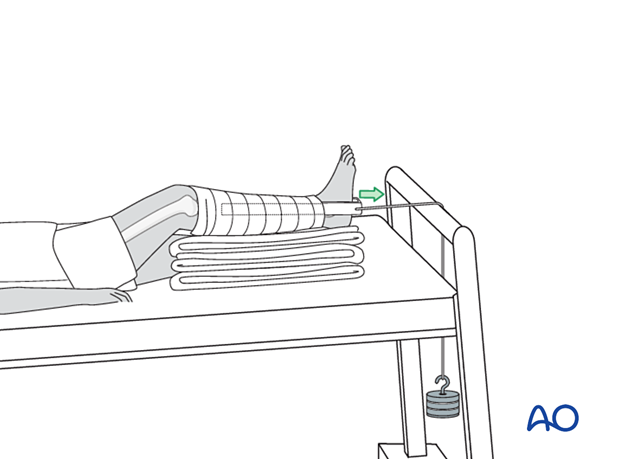
3. Skin traction
Skin traction may be used for pain relief but only for a few days maximum due to the likelihood of the adhesive wrap compromising the integrity of the skin.
Use about 2 kg of weight over the end of the bed for traction.
4. Mobilization
Mobilization starts when pain is tolerable; the patient may weight bear as tolerated with walking aids.