Dorsal approach to the 5th carpometacarpal joint
1. Indications
This approach is indicated for:
- Intraarticular fractures of the 5th metacarpal base
- Fracture-dislocations of the 5th carpometacarpal (CMC) joint
- Tendon avulsion fractures of the extensor carpi ulnaris
It can also be used for the rare displaced extraarticular fractures of the 5th metacarpal base.
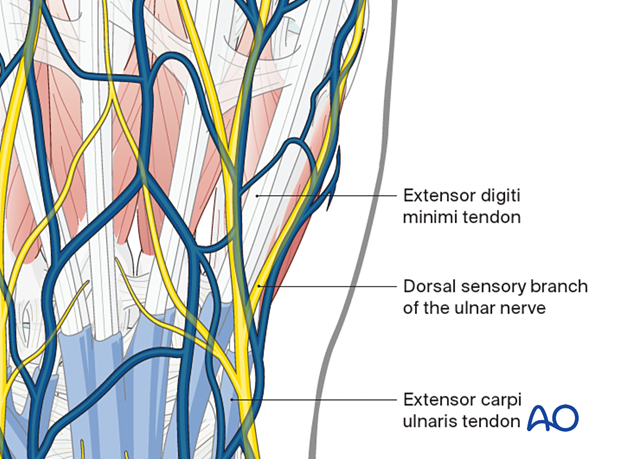
2. Surgical anatomy
The extensor tendons of the little finger converge slightly towards the center of the wrist joint.
The insertion of the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon is onto the ulnar side of the 5th metacarpal base.
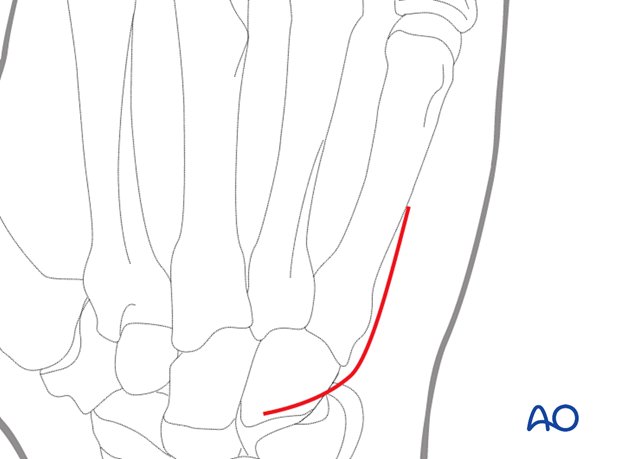
3. Skin incision
Perform a curved skin incision, running parallel to the 5th metacarpal on the dorsoulnar margin and curving radially over the hamate bone.
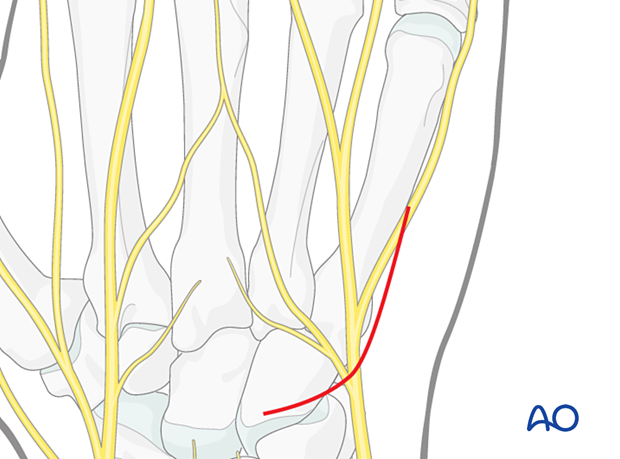
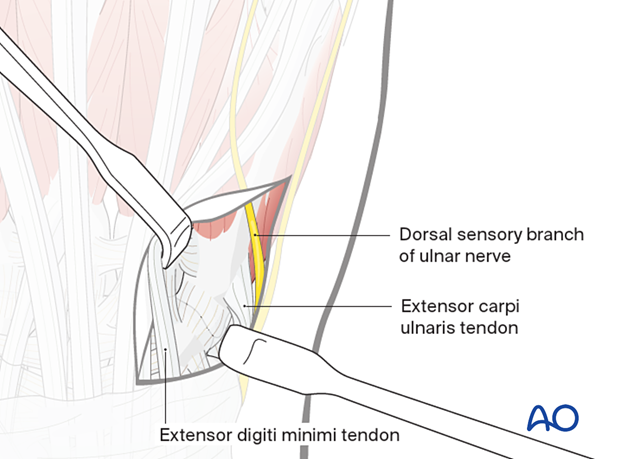
4. Retraction of extensor tendons
Retract the extensor tendons radially together with the surrounding loose connective tissue.
Retract the dorsal sensory branch of the ulnar nerve to the ulnar side, possibly together with the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon.
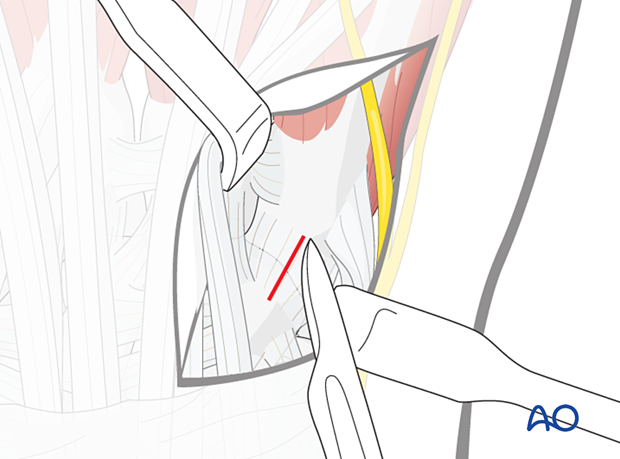
5. Capsulotomy
A longitudinal capsulotomy is made in case of intraarticular fractures.
Often, there is already a tear in the capsule, which can be extended.
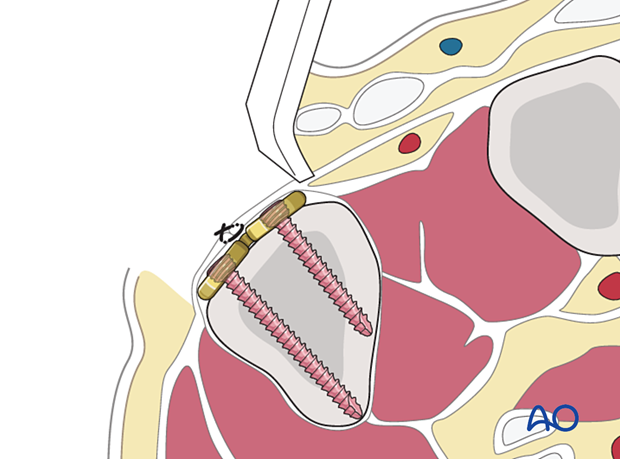
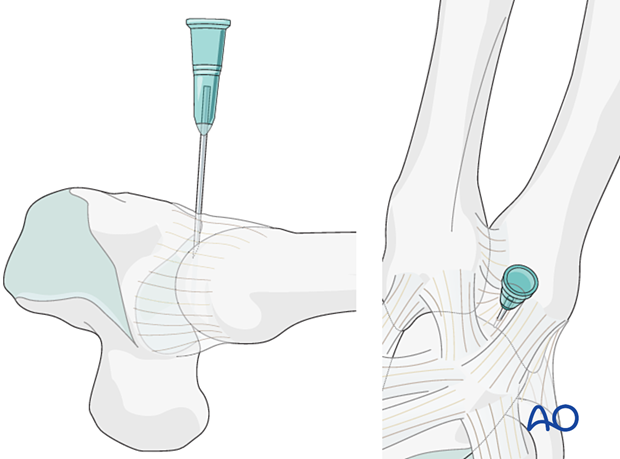
6. Pearl: marking the joint with a hypodermic needle
If a capsulotomy is not needed, mark the position of the joint with a hypodermic needle or a small K-wire. The position may be checked with an image intensifier. This helps to avoid inadvertent penetration of the joint with screws.
This technique is helpful with arthroscopically assisted surgery.
7. Wound closure
Cover the implant with the periosteum as far as possible; this helps minimize contact between the extensor tendons and the implant.
If an intertendinous connection has been cut, it should be repaired.