Complications and technical failures
1. Frequent complications
Common complications of these injuries are:
- Infection (general complication)
- Nonunion
- Malunion
- Restriction of joint movement
Nonunion and malunion may cause subsequent degenerative changes, eg, arthrosis. If these become symptomatic, then revision surgery may be indicated.
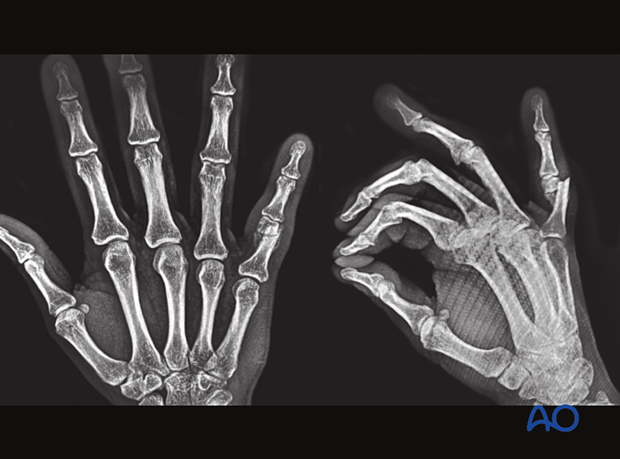
2. Nonunion
Signs for nonunion are pain and nonbridging healing on x-ray or CT in a period of 6–9 months after treatment.
Prevention
- Gentle operation technique to avoid damage to soft tissue and vascular supply
- Intraoperative assessment of construct stability
- Postoperative radiological assessment of reduction and fixation
Concomitant injuries should be addressed at the same time as the fracture to improve stability.
Appropriate postoperative management will help to protect the fracture.
Management of nonunion
Treatment of nonunions includes:
- Nonunion resection
- Bone graft application
- Stable internal fixation
3. Malunion
Prevention
- Anatomical reduction
- Stable fixation
- Intraoperative assessment of construct stability
- Postoperative radiological assessment of reduction and fixation
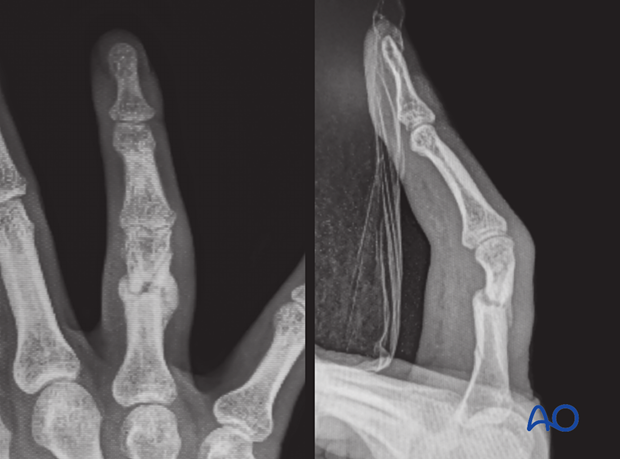
Management of malunion
- Corrective osteotomy
- Bone graft application, if necessary
- Stable internal fixation












